Clash of Christianities: Why Europe cannot understand Russia
Under an ubiquitous, toxic atmosphere of cognitive dissonance drenched in Russophobia, it’s absolutely impossible to have a meaningful discussion on finer points of Russian history and culture across the NATO space – a phenomenon I’m experiencing back in Paris right now, fresh from a long stint in Istanbul.
At best, in a semblance of civilized dialogue, Russia is pigeonholed in the reductionist view of a threatening, irrational, ever-expanding empire – a way more wicked version of Ancient Rome, Achaemenid Persia, Ottoman Turkey or Mughal India.
The fall of the USSR a little over three decades ago did hurl Russia back three centuries – to its borders in the 17th century. Russia, historically, had been interpreted as a secular empire – immense, multiple and multinational. This is all informed by history, very much alive even today in the Russian collective unconscious.
When Operation Z started I was in Istanbul – the Second Rome. I spent a considerable time of my late night walks around Hagia Sophia reflecting on the historical correlations of the Second Rome with the Third Rome – which happens to be Moscow, since the concept was first enounced at the start of the 16th century.
Later, back in Paris, banishment to soliloquy territory seemed inevitable until an academic pointed me to some substance, although heavily distorted by political correctness, available in the French magazine Historia.
There’s at least an attempt to discuss the Third Rome. The significance of the concept was initially religious before becoming political – encapsulating the Russian drive to become the leader of the Orthodox world in contrast with Catholicism. This has to be understood also in the context of pan-Slavic theories springing up under the first Romanov and then reaching their apogee in the 19th century.
Eurasianism – and its several declinations – treats the complex Russian identity as double-faced, between east and west. Western liberal democracies simply can’t understand that these ideas – infusing varied brands of Russian nationalism – do not imply hostility to “enlightened” Europe, but an affirmation of Difference (they could learn a bit from reading more Gilles Deleuze for that matter). Eurasianism also weighs on closer relations with Central Asia and necessary alliances, in various degrees, with China and Turkey.
A perplexed liberal west remains hostage to a vortex of Russian images which it can’t properly decode – from the two-headed eagle, which is the symbol of the Russian state since Peter the Great, to the Kremlin cathedrals, the St. Petersburg citadel, the Red Army entering Berlin in 1945, the May 9 parades (the next one will be particularly meaningful), and historical figures from Ivan the Terrible to Peter the Great. At best – and we’re talking academic level ‘experts’ – they identify all of the above as “flamboyant and confused” imagery.
The Christian/Orthodox divide
The apparently monolithic liberal west itself also cannot be understood if we forget how, historically, Europe is also a two-headed beast: one head may be tracked from Charlemagne all the way to the awful Brussels Eurocrat machine; and the other one comes from Athens and Rome, and via Byzantium/Constantinople (the Second Rome) reaches all the way to Moscow (the Third Rome).
Latin Europe, for the Orthodox, is seen as a hybrid usurper, preaching a distorted Christianity which only refers to St. Augustine, practicing absurd rites and neglecting the very important Holy Ghost. The Europe of Christian Popes invented what is considered a historical hydra – Byzantium – where Byzantines were actually Greeks living under the Roman Empire.
Western Europeans for their part see the Orthodox and the Christians from the East (see how they were abandoned by the west in Syria under ISIS and Al Qaeda) as satraps and a bunch of smugglers – while the Orthodox regard the Crusaders, the Teutonic chevaliers and the Jesuits – correctly, we must say – as barbarian usurpers bent on world conquest.
In the Orthodox canon, a major trauma is the fourth Crusade in 1204 which utterly destroyed Constantinople. The Frankish chevaliers happened to eviscerate the most dazzling metropolis in the world, which congregated at the time all the riches from Asia.
That was the definition of cultural genocide. The Frankish also happened to be aligned with some notorious serial plunderers: the Venetians. No wonder, from that historical juncture onwards, a slogan was born: “Better the Sultan’s turban than the Pope’s tiara.”
So since the 8th century, Carolingian and Byzantine Europe were de facto at war across an Iron Curtain from the Baltics to the Mediterranean (compare it with the emerging New Iron Curtain of Cold War 2.0). After the barbarian invasions, they neither spoke the same language nor practiced the same writing, rites or theology.
This fracture, significantly, also trespassed Kiev. The west was Catholic – 15% of Greek catholics and 3% of Latins – and in the center and the east, 70% Orthodox, who became hegemonic in the 20th century after the elimination of Jewish minorities by mainly the Waffen-SS of the Galicia division, the precursors of Ukraine’s Azov batallion.
Constantinople, even in decline, managed to pull off a sophisticated geo-strategic game to seduce the Slavs, betting on Muscovy against the Catholic Polish-Lithuanian combo. The fall of Constantinople in 1453 allowed Muscovy to denounce the treason of Greeks and Byzantine Armenians who rallied around the Roman Pope, who badly wanted a reunified Christianity.
Afterward, Russia ends up constituting itself as the only Orthodox nation that did not fall under Ottoman domination. Moscow regards itself – as Byzantium – as a unique symphony between spiritual and temporal powers.
Third Rome becomes a political concept only in the 19th century – after Peter the Great and Catherine the Great had vastly expanded Russian power. The key concepts of Russia, Empire and Orthodoxy are fused. That always implies Russia needs a ‘near abroad’ – and that bears similarities with Russian President Vladimir Putin’s vision (which, significantly, is not imperial, but cultural).
As the vast Russian space has been in constant flow for centuries, that also implies the central role of the concept of encirclement. Every Russian is very much aware of territorial vulnerability (remember, for starters, Napoleon and Hitler). Once the western borderland is trespassed, it’s an easy ride all the way to Moscow. Thus, this very unstable line must be protected; the current correlation is the real threat of Ukraine made to host NATO bases.
Onward to Odessa
With the fall of the USSR, Russia found itself in a geopolitical situation last encountered in the 17th century. The slow and painful reconstruction was spearheaded from two fronts: the KGB – later FSB – and the Orthodox church. The highest-level interaction between the Orthodox clergy and the Kremlin was conducted by Patriarch Kirill – who later became Putin’s minister of religious affairs.
Ukraine for its part had become a de facto Moscow protectorate way back in 1654 under the Treaty of Pereyaslav: much more than a strategic alliance, it was a natural fusion, in progress for ages by two Orthodox Slav nations.
Ukraine then falls under the Russian orbit. Russian domination expands until 1764, when the last Ukrainian hetman (commander-in-chief) is officially deposed by Catherine the Great: that’s when Ukraine becomes a province of the Russian empire.
As Putin made it quite clear this week: “Russia cannot allow the creation of anti-Russian territories around the country.” Operation Z will inevitably encompass Odessa, founded in 1794 by Catherine the Great.
The Russians at the time had just expelled the Ottomans from the northwest of the Black Sea, which had been successively run by Goths, Bulgars, Hungarians and then Turkish peoples – all the way to the Tatars. Odessa at the start was peopled, believe it or not, by Romanians who were encouraged to settle there after the 16th century by the Ottoman sultans.
Catherine chose a Greek name for the city – which at the start was not Slav at all. And very much like St. Petersburg, founded a century earlier by Peter the Great, Odessa never stopped flirting with the west.
Tsar Alexander I, in the early 19th century, decides to turn Odessa into a great trading port – developed by a Frenchman, the Duke of Richelieu. It was from the port of Odessa that Ukrainian wheat started to reach Europe. By the turn of the 20th century, Odessa is truly multinational – after having attracted, among others, the genius of Pushkin.
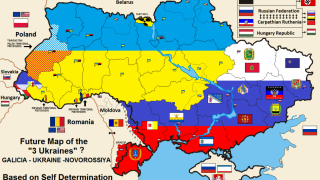
Odessa is not Ukrainian: it’s an intrinsic part of the Russian soul. And soon the trials and tribulations of history will make it so again: as an independent republic; as part of a Novorossiya confederation; or attached to the Russian Federation. The people of Odessa will decide.