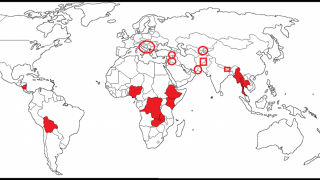
Everybody wants to hop on the BRICS Express
Let’s start with what is in fact a tale of Global South trade between two members of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO). At its heart is the already notorious Shahed-136 drone – or Geranium-2, in its Russian denomination: the AK-47 of postmodern aerial warfare.
The US, in yet another trademark hysteria fit rife with irony, accused Tehran of weaponizing the Russian Armed Forces. For both Tehran and Moscow, the superstar, value-for-money, and terribly efficient drone let loose in the Ukrainian battlefield is a state secret: its deployment prompted a flurry of denials from both sides. Whether these are made in Iran drones, or the design was bought and manufacturing takes place in Russia (the realistic option), is immaterial.
The record shows that the US weaponizes Ukraine to the hilt against Russia. The Empire is a de facto war combatant via an array of “consultants,” advisers, trainers, mercenaries, heavy weapons, munitions, satellite intel, and electronic warfare. And yet imperial functionaries swear they are not part of the war. They are, once again, lying.
Welcome to yet another graphic instance of the “rules-based international order” at work. The Hegemon always decides which rules apply, and when. Anyone opposing it is an enemy of “freedom,” “democracy,” or whatever platitude du jour, and should be – what else – punished by arbitrary sanctions.
In the case of sanctioned-to-oblivion Iran, for decades now, the result has been predictably another round of sanctions. That’s irrelevant. What matters is that, according to Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), no less than 22 nations – and counting – are joining the queue because they also want to get into the Shahed groove.
Even Leader of the Islamic Revolution, Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, gleefully joined the fray, commenting on how the Shahed-136 is no photoshop.
The race towards BRICS+
What the new sanctions package against Iran really “accomplished” is to deliver an additional blow to the increasingly problematic signing of the revived nuclear deal in Vienna. More Iranian oil on the market would actually relieve Washington’s predicament after the recent epic snub by OPEC+.
A categorical imperative though remains. Iranophobia – just like Russophobia – always prevails for the Straussians/neo-con war advocates in charge of US foreign policy and their European vassals.
So here we have yet another hostile escalation in both Iran-US and Iran-EU relations, as the unelected junta in Brussels also sanctioned manufacturer Shahed Aviation Industries and three Iranian generals.
Now compare this with the fate of the Turkish Bayraktar TB2 drone – which unlike the “flowers in the sky” (Russia’s Geraniums) has performed miserably in the battlefield.
Kiev tried to convince the Turks to use a Motor Sich weapons factory in Ukraine or come up with a new company in Transcarpathia/Lviv to build Bayraktars. Motor Sich’s oligarch President Vyacheslav Boguslayev, aged 84, has been charged with treason because of his links to Russia, and may be exchanged for Ukrainian prisoners of war.
In the end, the deal fizzled out because of Ankara’s exceptional enthusiasm in working to establish a new gas hub in Turkey – a personal suggestion from Russian President Vladimir Putin to his Turkish counterpart Recep Tayyip Erdogan.
And that bring us to the advancing interconnection between BRICS and the 9-member Shanghai Cooperation Council (SCO) – to which this Russia-Iran instance of military trade is inextricably linked.
The SCO, led by China and Russia, is a pan-Eurasian institution originally focused on counter-terrorism but now increasingly geared towards geoeconomic – and geopolitical – cooperation. BRICS, led by the triad of Russia, India, and China overlaps with the SCO agenda geoeconomically and geopoliticallly, expanding it to Africa, Latin America and beyond: that’s the concept of BRICS+, analyzed in detail in a recent Valdai Club report, and fully embraced by the Russia-China strategic partnership.
The report weighs the pros and cons of three scenarios involving possible, upcoming BRICS+ candidates:
First, nations that were invited by Beijing to be part of the 2017 BRICS summit (Egypt, Kenya, Mexico, Thailand, Tajikistan).
Second, nations that were part of the BRICS foreign ministers’ meeting in May this year (Argentina, Egypt, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Nigeria, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Senegal, Thailand).
Third, key G20 economies (Argentina, Indonesia, Mexico, Saudi Arabia, Turkiye).
And then there’s Iran, which has already already shown interest in joining BRICS.
South African President Cyril Ramaphosa has recently confirmed that “several countries” are absolutely dying to join BRICS. Among them, a crucial West Asia player: Saudi Arabia.
What makes it even more astonishing is that only three years ago, under former US President Donald Trump’s administration, Crown Prince Muhammad bin Salman (MbS) – the kingdom’s de fact ruler – was dead set on joining a sort of Arab NATO as a privileged imperial ally.
Diplomatic sources confirm that the day after the US pulled out of Afghanistan, MbS’s envoys started seriously negotiating with both Moscow and Beijing.
Assuming BRICS approves Riyadh’s candidacy in 2023 by the necessary consensus, one can barely imagine its earth-shattering consequences for the petrodollar. At the same time, it is important not to underestimate the capacity of US foreign policy controllers to wreak havoc.
The only reason Washington tolerates Riyadh’s regime is the petrodollar. The Saudis cannot be allowed to pursue an independent, truly sovereign foreign policy. If that happens, the geopolitical realignment will concern not only Saudi Arabia but the entire Persian Gulf.
Yet that’s increasingly likely after OPEC+ de facto chose the BRICS/SCO path led by Russia-China – in what can be interpreted as a “soft” preamble for the end of the petrodollar.
The Riyadh-Tehran-Ankara triad
Iran made known its interest to join BRICS even before Saudi Arabia. According to Persian Gulf diplomatic sources, they are already engaged in a somewhat secret channel via Iraq trying to get their act together. Turkey will soon follow – certainly on BRICS and possibly the SCO, where Ankara currently carries the status of extremely interested observer.
Now imagine this triad – Riyadh, Tehran, Ankara – closely joined with Russia, India, China (the actual core of the BRICS), and eventually in the SCO, where Iran is as yet the only West Asian nation to be inducted as a full member.
The strategic blow to the Empire will go off the charts. The discussions leading to BRICS+ are focusing on the challenging path towards a commodity-backed global currency capable of bypassing US dollar primacy.
Several interconnected steps point towards increasing symbiosis between BRICS+ and SCO. The latter’s members states have already agreed on a road map for gradually increasing trade in national currencies in mutual settlements.
The State Bank of India – the nation’s top lender – is opening special rupee accounts for Russia-related trade.
Russian natural gas to Turkey will be paid 25 percent in rubles and Turkish lira, complete with a 25 percent discount Erdogan personally asked of Putin.
Russian bank VTB has launched money transfers to China in yuan, bypassing SWIFT, while Sberbank has started lending out money in yuan. Russian energy behemoth Gazprom agreed with China that gas supply payments should shift to rubles and yuan, split evenly.
Iran and Russia are unifying their banking systems for trade in rubles/rial.
Egypt’s Central Bank is moving to establish an index for the pound – through a group of currencies plus gold – to move the national currency away from the US dollar.
And then there’s the TurkStream saga.
That gas hub gift
Ankara for years has been trying to position itself as a privileged East-West gas hub. After the sabotage of the Nord Streams, Putin has handed it on a plate by offering Turkey the possibility to increase Russian gas supplies to the EU via such a hub. The Turkish Energy Ministry stated that Ankara and Moscow have already reached an agreement in principle.
This will mean in practice Turkey controlling the gas flow to Europe not only from Russia but also Azerbaijan and a great deal of West Asia, perhaps even including Iran, as well as Libya in northeast Africa. LNG terminals in Egypt, Greece and Turkiye itself may complete the network.
Russian gas travels via the TurkStream and Blue Stream pipelines. The total capacity of Russian pipelines is 39 billion cubic meters a year.

Map of Russian gas route via Turkey
TurkStream was initially projected as a four-strand pipeline, with a nominal capacity of 63 million cubic meters a year. As it stands, only two strands – with a total capacity of 31,5 billion cubic meters – have been built.
So an extension in theory is more than feasible – with all the equipment made in Russia. The problem, once again, is laying the pipes. The necessary vessels belong to the Swiss Allseas Group – and Switzerland is part of the sanctions craze. In the Baltic Sea, Russian vessels were used to finish building Nord Stream 2. But for a TurkStream extension, they would need to operate much deeper in the ocean.
TurkStream would not be able to completely replace Nord Stream; it carries much smaller volumes. The upside for Russia is not being canceled from the EU market. Evidently Gazprom would only tackle the substantial investment on an extension if there are ironclad guarantees about its security. And there’s the additional drawback that the extension would also carry gas from Russia’s competitors.
Whatever happens, the fact remains that the US-UK combo still exerts a lot of influence in Turkey – and BP, Exxon Mobil, and Shell, for instance, are actors in virtually every oil extraction project across West Asia. So they would certainly interfere on the way the Turkish gas hub functions, as well on determining the gas price. Moscow has to weigh all these variables before committing to such a project.
NATO, of course, will be livid. But never underestimate hedging bet specialist Sultan Erdogan. His love story with both the BRICS and the SCO is just beginning.