Terror from Balochistan: a menacing tool to disrupt Sino-Pakistani economics
This is the concise story of how a suicide bombing may carry the potential to subvert the whole, ongoing, complex process of Eurasia integration.
Recently, the Balochistan Liberation Movement (BLA) had released an ISIS-influenced video threatening “Chinese officials and installations” in Pakistan’s vast province.
Yet what actually happened in late April was a suicide bombing outside of the University of Karachi’s Confucius Institute – not Balochistan – and targeting Chinese teachers, not “officials and installations.”
The suicide bomber was a woman, Shaari Baloch, alias Bramsh, who detonated her vest just as a van carrying Institute staff members approached the entrance. The attack was claimed by the BLA’s Majeed Brigade, which stressed that this was the first time they used a female suicide bomber.
Shaari Baloch was a schoolteacher with a Zoology degree, enrolled to pursue a second Master’s degree, married to a dentist and professor at Makran Medical College in her hometown of Turbat, in southern Balochistan. Her three brothers include a doctor, a deputy director at a government-funded project, and a civil servant. So Shaari Baloch was far from being a mere destitute online-indoctrinated Salafi-jihadi.
The Pakistani Foreign Office had to stress the obvious: this was a “direct attack on the Pakistan-China friendship and ongoing cooperation,” always qualified, by both sides, as “iron brothers.” Pakistan is an absolutely key node of the Chinese Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) to connect the Eurasian landmass.
This was no standard terrorist attack. Its reverberations are immense – not only in one of Pakistan’s provinces and South Asia regionally, but for the whole of Eurasia. It may be a harbinger of serious turbulence ahead.
Shaari Baloch’s act of desperation should be seen, to start with, as the embodiment of a deep-seated Baloch alienation felt by the educated middle classes, from lawyers and traders to students, constantly permeating the complex relationship with a distant Islamabad. A significant part of the puzzle is that 26 Pakistani intel agencies never saw it coming.
Baloch leaders instantly made the point that the best possible reaction would be to call a Grand Jirga – modeled on the Shahi Jirga practiced at the time of the partition of the subcontinent – that would unite all tribal elders to address the most pressing local grievances.
Round up the usual suspects
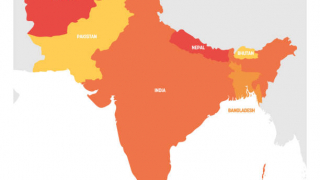
Balochistan, geostrategically, is as valuable as rare earth minerals: an immense desert positioned east of Iran, south of Afghanistan, and boasting three Arabian Sea ports, including Gwadar, practically at the mouth of the strategic Strait of Hormuz.
Comprising nearly 48 percent of Pakistan’s area, Balochistan is rich in uranium and copper, potentially very rich in oil, produces more than one-third of Pakistan’s natural gas, and sparsely populated. The Baloch account for the majority of the population, followed by Pashtuns. Quetta, the large provincial capital, for years was considered Taliban Central by the Pentagon.
Gwadar, the port built by China on the southwestern Balochistan coast of the Arabian Sea – directly across from Oman – is the absolute key node of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), and doubles as the essential link in a never-ending pipeline saga. The Iran-Pakistan-India (IPI) gas pipeline, previously known as the “peace pipeline,” with plans to cross from Iranian to Pakistani Balochistan (India still has not made up its mind) is absolute anathema to Washington since the George W. Bush era.
CPEC remains an endless source of controversy even inside Pakistan. Beyond all the links planned between Gwadar and Xinjiang by the year 2030, most of this ambitious connectivity corridor deals with energy, industrial zones and road and rail projects in different parts of the country – an overall improvement of its lagging infrastructure. The Chinese, for years, have quipped that in fact “all of Pakistan is a corridor.”
The US security establishment, predictably, has been planning for years to instrumentalize an insurgency in Balochistan to – what else – “disrupt” first the possibility of an energy pipeline from Gwadar to Xinjiang, and then the overall CPEC project. Usual suspects like the US’s National Endowment for Democracy (NED) are very much present in Balochistan. WikiLeaks had revealed a great deal of the game back in 2015.
A Carnegie Institute report noted how “many Baloch nationalist leaders now come from the urbanized districts of Kech, Panjgur, and Gwadar (and to a lesser extent from Quetta, Khuzdar, Turbat, Kharan, and Lasbela). They are well connected to Karachi and Gulf cities, where tribal structures are non-existent. In fact, while there is violence all over the province, the insurgency seems to concentrate mainly in these urbanized areas.”
Suicide bomber Shaari Baloch came from Turbat, the province’s second largest city, where the BLA is very much active. From the point of view of the usual suspects, these are choice assets, especially after the death of important tribal leaders such as Akbar Bugti. The report duly noted how “the educated and middle-class Baloch youth are in the forefront” of the insurgency.
The anti-China instrumentalization of the BLA also ties in with the regime-change parliament operation in Islamabad that recently deposed former prime minister Imran Khan, who was always a fierce adversary of the American “Forever War” in Afghanistan. Khan resolutely denied Pakistan’s use in “over the horizon” US military ops: that was one of the key reasons for him to be ousted.
Now, with a pliant, Washington-approved, new regime in town, a miracle has just happened: the Pentagon is about to clinch a formal agreement with Islamabad to use Pakistani airspace to – what else – keep interfering in Afghanistan.
Beijing, as well as other members of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), won’t be amused. Only weeks before the white coup, Khan had met with Chinese President Xi Jinping and once again underscored how Pakistan and China are “iron brothers.”
Imran Khan was a serious thorn in the side of the west because he kept impressing on Pakistanis that the Forever War in Afghanistan was militarily unwinnable. He knew how all the proxies – including the BLA – that destabilized both Afghanistan and Pakistan for decades were, and continue to be, part of US covert operations.
Not an Iran-India plot
Balochistan is as deeply tribal as the Pashtun tribal areas. Local tribal chiefs can be as ultra-conservative as Islamabad is neglectful (and they are not exactly paragons of human rights either). Most tribes though bow to Islamabad’s authority – except, first and foremost, the Bugti.
And then there’s the Balochistan Liberation Army (BLA), which both Washington and London used to brand as a terrorist group, and then forgot about it. The BLA operated for years out of Kandahar in Afghanistan (only two hours away from Quetta), and already in the previous decade – simultaneous to the announcement of the New Silk Roads and CPEC – stressed it was getting ready to attack non-Balochis (code for the government in Islamabad as well as Chinese foreigners).
Balochis are inclined to consider the BLA as a resistance group. But Islamabad has always denied it, saying their support is not beyond 10 percent of the provincial population.
An ample controversy has raged in Pakistan for years on whether the BLA was totally hijacked by the CIA, the MI6 and the Mossad. During a 2006 visit to Iran, I was prevented from going to the Sistan-Balochistan province in southeast Iran because, according to Tehran’s version, infiltrated CIA from Pakistani Balochistan were involved in covert, cross-border attacks. It was no secret to anyone in the region that since 9/11 the US virtually controlled the Baloch air bases in Dalbandin and Panjgur.
In October 2001, while waiting for an opening to cross to Kandahar from Quetta, I spent quite some time with a number of BLA associates and sympathizers. They described themselves as “progressive, nationalist, anti-imperialist” (and that would make them difficult to be co-opted by the US). They were heavily critical of “Punjabi chauvinism,” and always insisted the region’s resources belong to Balochis first; that was their rationale for attacks on gas pipelines.
Stressing an atrocious, provincial literacy rate of only 16 percent (“It’s government policy to keep Balochistan backward”), they resented the fact that most people still lacked drinking water. They claimed support from at least 70 percent of the Baloch population (“Whenever the BLA fires a rocket, it’s the talk of the bazaars”). They also claimed to be united, and in coordination with Iranian Balochis. And they insisted that “Pakistan had turned Balochistan into a US cantonment, which affected a lot the relationship between the Afghan and Baloch peoples.”
Two decades later, and after the whole ISIS saga in Syria and Iraq, it’s a completely different story. BLA sympathizers may still be prepared to remain within a Pakistani confederation, although with infinitely more autonomy. But now they seem to be willing to use western imperial help to strike not only at the central government in Islamabad, but also at the “near abroad” foreign profiteer (China).
After the Karachi suicide bombing, a narrative started to emerge in some Pakistani circles that Iran and India were in cahoots to destabilize Balochistan.
That makes absolutely no sense. Both Tehran and Islamabad are tightly linked to Beijing through several nodes of the New Silk Roads. Iran would draw less than zero benefit to collude with India to destabilize an area that borders Afghanistan, especially when the SCO is fully engaged in incorporating Kabul into the Eurasia integration process. Moreover, the IPI has its best chances ever to come to fruition in the near future, consolidating an umbilical cord from Southwest Asia to South Asia.
During the late years of Barack Obama’s administration, the BLA, though still a fringe group with a political wing and a military wing, was regrouping and rearming, while the chief minister of Balochistan, Nawab Raisani, was suspected of being a CIA asset (there was no conclusive proof).
Already at the time, the fear in Islamabad was that the government had taken its eye off the Balochistan ball – and that the BLA was about to be effectively used by the US for balkanization purposes. That seems to be the picture right now. Yet the heart of the matter – glaringly expressed by the Karachi suicide bombing – is that Islamabad still remains impervious to the key Baloch grievance: we want to profit from our natural wealth, and we want autonomy.